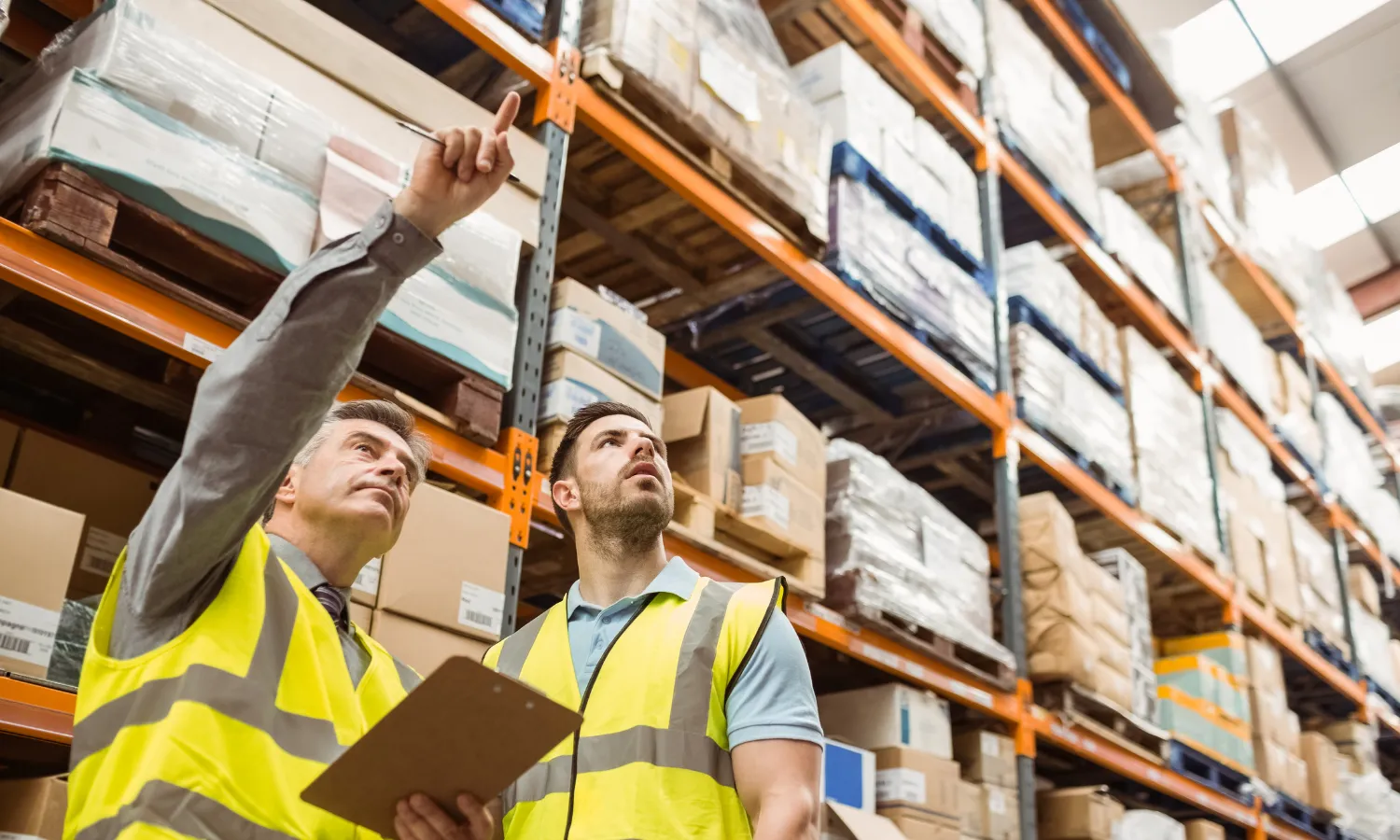
Situation
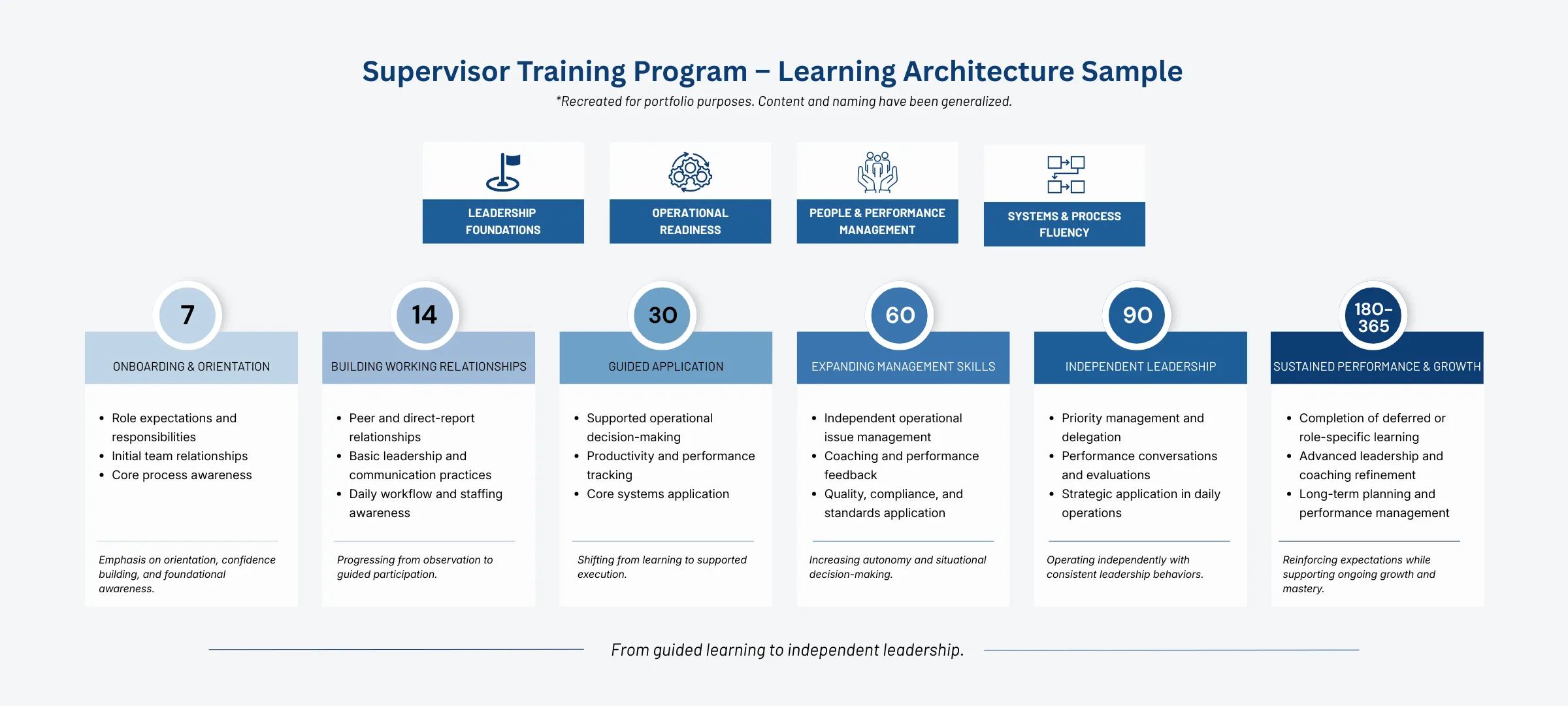
High turnover among warehouse supervisors was impacting consistency in operations and contributing to frontline associate dissatisfaction. A company-wide needs assessment revealed several issues with supervisor onboarding and development:
- No consistent standard for success across facilities.
- New supervisors felt overwhelmed by the volume of information in their first weeks.
- Many processes were learned informally, leading to inconsistent practices.
- Technical troubleshooting (e.g., warehouse management systems) often delayed operations due to lack of formal training.
- Leadership and soft skills were underdeveloped compared to technical and operational strengths.
- Previous resources (e.g., binders and checklists) were inconsistently used, with no accountability.
The result: supervisors took an average of 6–8 months to reach full productivity.